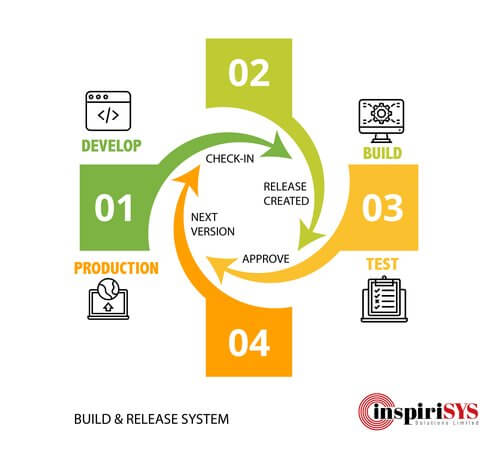
Software industry is constantly pushing its boundaries to shorten the cycle times in the development and operations process. Developers were working in isolation to get rid of the build failures that break the entire system. This approach changed after the introduction of automated build and release system. The methodology of managing, planning, scheduling and controlling a software-build is widely called Build and Release Management. The process is handled through different stages and software environments that include testing and deploying software releases. The below approach entails continuous integration, delivery, development, and test automation.
Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration empowers developers to integrate code into a shared repository. Integration happens frequently and each integration is verified by automated builds and tests. It swiftly identifies the defects in the code and enables developers to correct as soon as possible.
Continuous Delivery
Continuous delivery ensures a sustainable way to add brand new features, change configurations, fix bugs, do experience and deliver them to the end-user seamlessly. It allows the development team to produce or release a software update in short life cycles.
Test Automation
Test automation is to replace mundane and repeated test executions. In this approach, test automation tools are used to execute the test and compare the test results with the expected and predicted outcome.
Continuous Deployment
Any code that passes through the test automation phase is automatically released into the production environment. Continuous Deployment enables the end-users to access the features that are ready to release.
Technical strands behind automated build and release system
Continuous Integration using Jenkins
Continuous integration allows the developers to continuously integrate the code into the whole system. It also ensures the reliability of the code that is not corrupting the system at any point in time. Furthermore, it helps to eliminate integration issues since the agile methodology enables the developers to correct instantaneously.
One of the widely used continuous integration tools is the Jenkins CI Server. The Jenkins jobs can be used to execute a predefined set of steps (build, release, test, deployment) and if any of the steps fail, can immediately notify the developers and get it corrected.
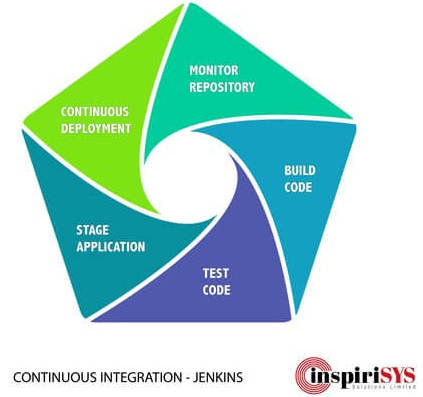
Each of the Jenkins job has the following sections:
1. Source code Management: Check-out the source code from the repository for building. The default SCM tools supported are SVN, Git.
2. Build Triggers - Configure when the build needs to be triggered, Options are polling SCM, scheduled build, build after other projects are built or using scripts.
3. Build Environment - Configure the build environment - workspace, timestamp and environment variable related settings.
4. Build Section - Configure the build steps - based on the system either we can execute windows batch command or Linux shell command.
5. Post Build Section - Configure actions that need to be taken after the build - like archiving artifacts, email notification and triggering other jobs.
Process Automation using Scripting Languages
The entire build and release process are automated using various scripting languages as per the requirement. Build process automation in windows environment was designed using batch script, Python, Jinja2 template engine and PowerShell. Similarly, the Linux environment automation was accomplished using Shell script and Mac process automation was implemented using Ruby scripting.
Source Code Management Tools
Source Code Management and version control systems ensure all members of a team stay on top of changes to source code and related files. They are used to give versions/revisions to the program. Each version comprises a timestamp and the owner of the change. Different versions can be compared and merged. Hence SCM is also called version control, revision control or source control.
Enterprise automated build system managed by Inspirisys
ISL product engineering team has implemented a build system for Enterprise solutions that match the requirements of enterprises. We have an easy to use tool for automating instantiation process. With this, all required files of a printing device get generated with a simple command-line call. Since the tool supports the command line call that easily integrated with the build process, files will be dynamically generated before the build process.
We have developed a flexible build framework using python and MSBuild scripts. Automated tagging after the build process and regeneration of a previous build are the key features.
With this build, we fix the issue of compile errors while integrating the code. It is intended for early catching of compile errors. We design Jenkins job to invoke the build whenever a developer check-in his changes to the version control system. It ensures the buildable code in the version control system. If a build failed, an email will be sent to the developer to fix the issue.
Click here to talk to an expert!