Industry 4.0 is the new beginning of the technological era. It is characterized by factories augmented with wireless connectivity and sensors. Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), Internet of Things (IoT), Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Cloud Computing, Cognitive Computing, Artificial Intelligence (AI) are the backbone technologies of Industry 4.0. Their combined capabilities are giving life to the concept of smart manufacturing, smart factory and lights out manufacturing or dark factories. This entire industrial revolution is in the ability of systems to communicate and cooperate with each other and with humans in real-time internally and across the entire product lifecycle. Most of the business owners are mystified by the complexity of industry 4.0 and think that only big enterprises can harness its benefits. But on the flip side, it is less complicated. Because the cost of IoT technology is reducing drastically over a period of time. With 60% decrease in sensors cost over the last decade, the adoption of IoT considerably increased. But before harnessing any kind of technological advancements, it is a necessity to know its background.
Types of Industrial Revolution
Industry 1.0

It is commonly termed as the first industrial revolution. It started when there was a transition from hand production to machine production. It was a result of the use of steam power and water power. But implementation of technologies took a long time between 1760 and 1820 or 1840 in Europe and the US. It contributed significant consequences to the textile industry who were the early adopters of this revolution. It also made a positive impact on the British manufacturing industry.
Industry 2.0
Between 1870 and 1914, industries stepped into the next industrial revolution called the Second industrial revolution and technological revolution. It was made possible with the implementation of extensive railroad networks and telegraph. This enabled faster transfer of people and ideas. Factory electrification played a major role in modernizing the production line. This is hailed as a period of great economic growth. There was a vast increase in productivity. But it surged unemployment all over the world since many workers were replaced by machines in factories.
Industry 3.0
The third industrial revolution happened in the late 20th century after the end of two big wars. It is called a digital revolution. It was the beginning of more advanced digital developments. It laid the next significant progress in the development of communication technologies with supercomputers. There was extensive use of computer and communication technologies in the production process.
Industry 4.0 – The term
 The term Industry 4.0 or I4.0 or I4 was originated in 2011 by a project in the high-tech strategy of the German government which promoted computerization of the manufacturing sector. It was publicly introduced in the same year at Hannover Fair. In October 2012, a working group on industry 4.0 presented a set of industry 4.0 implementation to the German federal government. So, industry 4.0 workgroup members and partners were recognized as the founding fathers and driving force behind industry 4.0.
The term Industry 4.0 or I4.0 or I4 was originated in 2011 by a project in the high-tech strategy of the German government which promoted computerization of the manufacturing sector. It was publicly introduced in the same year at Hannover Fair. In October 2012, a working group on industry 4.0 presented a set of industry 4.0 implementation to the German federal government. So, industry 4.0 workgroup members and partners were recognized as the founding fathers and driving force behind industry 4.0.
Goals of Industry 4.0
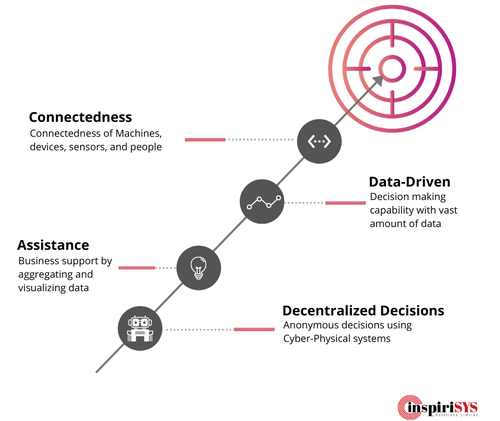
Connectedness
- The connectedness of Machines, devices, sensors, and people
- Establishment of holistic device communication via the Internet of things and the Internet of People
Data-driven
- Appropriate decision-making capability with a vast amount of useful data from different sources across the manufacturing process
Assistance Systems
- Business support by aggregating and visualizing data
- Critical decision-making capabilities to solve urgent problems on short notice
Decentralized decisions
- Ability to make autonomous decisions using Cyber-Physical systems
Components of Industry 4.0
The contributing digital technologies for many of the components of industry 4.0 are mobile devices, Internet of Things, location detection technologies, advanced human-machine interfaces, authentication, and fraud detection, 3D printing, smart sensors, big data analytics and advanced algorithms, multilevel customer interaction, and customer profiling, Augmented Reality, Fog, Edge and Computing, Data visualization and triggered real-time training. These technologies are summarized into the below 4 components
- Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Cloud Computing
- Cognitive Computing
Impact of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is aimed to replace inefficient traditional automation with automatically coordinated automation using the Internet of Things together with Artificial Intelligence. IoT is expected to impact many areas in the manufacturing and administration sector. Most notably, Services and business models, reliability and continuous productivity, IT Security, Machine Safety, Product lifecycles, Industry value chain, workers’ education, and skills, Socio-economic factors on the supply chain of many industries are going to harness its benefits. Industry 4.0 creates an entirely new way of serving existing needs. There are major shifts on the demand side, since growing transparency, consumer engagement and new patterns of consumer behaviour force companies to adapt the way they design, market and deliver the products and services.
Challenges of Industry 4.0
- The lack of unified leadership across the unit coordination is a major setback for a company to harness the benefits of Industry 4.0. Any kind of technological advancement in the production unit needs a unified approval from C level executives.
- When people choose a third-party vendor, the hosting of a vast amount of data generated by the IoT sensors raises data ownership concerns.
- Most companies lack courage to launch a radical digitalization plan.
- Lack of in-house talent to support the digital development hinders the deployment of industry 4.0 initiatives.
- Production facilities are chaotic in nature. It is not necessary to have compatibility with every device and machine on the supply chain. This incompatibility impedes data integration.
- Cyber-attacks are the biggest threat for IoT devices. It is accelerating at an unprecedented rate.
How Inspirisys can help to overcome the industry 4.0 challenges?
Inspirisys is a leading IoT solutions provider in India. Our IoT solution portfolio and profound technology experience enable organizations to accelerate their ideas and innovation to the market, immediately translating IT savings into a business advantage. The domain expertise we bring to the table allows the organizational leaders to make better decisions. We provide state-of-the-art data security solutions across the IoT spectrum to ensure safe and secured connectedness. Some of our IoT solutions are
- IoT Application Design & Development
- IoT Application Re-engineering, support and maintenance
- IoT Rapid Prototyping
- Device & Sensor Gateway identification and evaluation
- IoT cloud integration
Click here to talk to an IoT expert.







