The threat landscape is changing. Over the past decade, organizations have witnessed many Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) aimed to infiltrate the secured network, exfiltrate business data and thus damage the organization’s reputation. Cyber-attacks have evolved over a period of time and adopted modern technologies to outbreak effective defence mechanisms. Now they progressed to the extent that they can counter attack any kind of defensive countermeasures. One such perilous attack that intrudes into a system and mines private data is Advanced Persistent Threat. APT is the most advanced cyber threat in the security landscape. The reason why it is called an Advanced Persistent Threat is:
Advanced
It uses extremely advanced techniques and technologies to intrude into a system. It adjusts with any kind of defensive countermeasures.
Persistent
It continuously spectates the target and extracts critical information. The goal of an APT attack is to exfiltrate specific information from the system. It waits for the right opportunity and deploys the attack strategy. The strategy is devised for multi-month and even years of intrusion.
Threat
It leaves a huge impact by stealing intellectual properties or critical information. Organizations are unaware of this attack until damage to the critical data is noticed. It poses severity by not leaving a clue on what was stolen and what would the potential future impact.
7 Phases of Advanced Persistent Threat
To successfully intrude into an organization and steal a piece of specific information, the APT attack has to undergo a chain of 7 phases. The attack can be potentially stopped when any one of these 7 phases is prevented. For the reason that each phase depends on its previous phase to move forward.
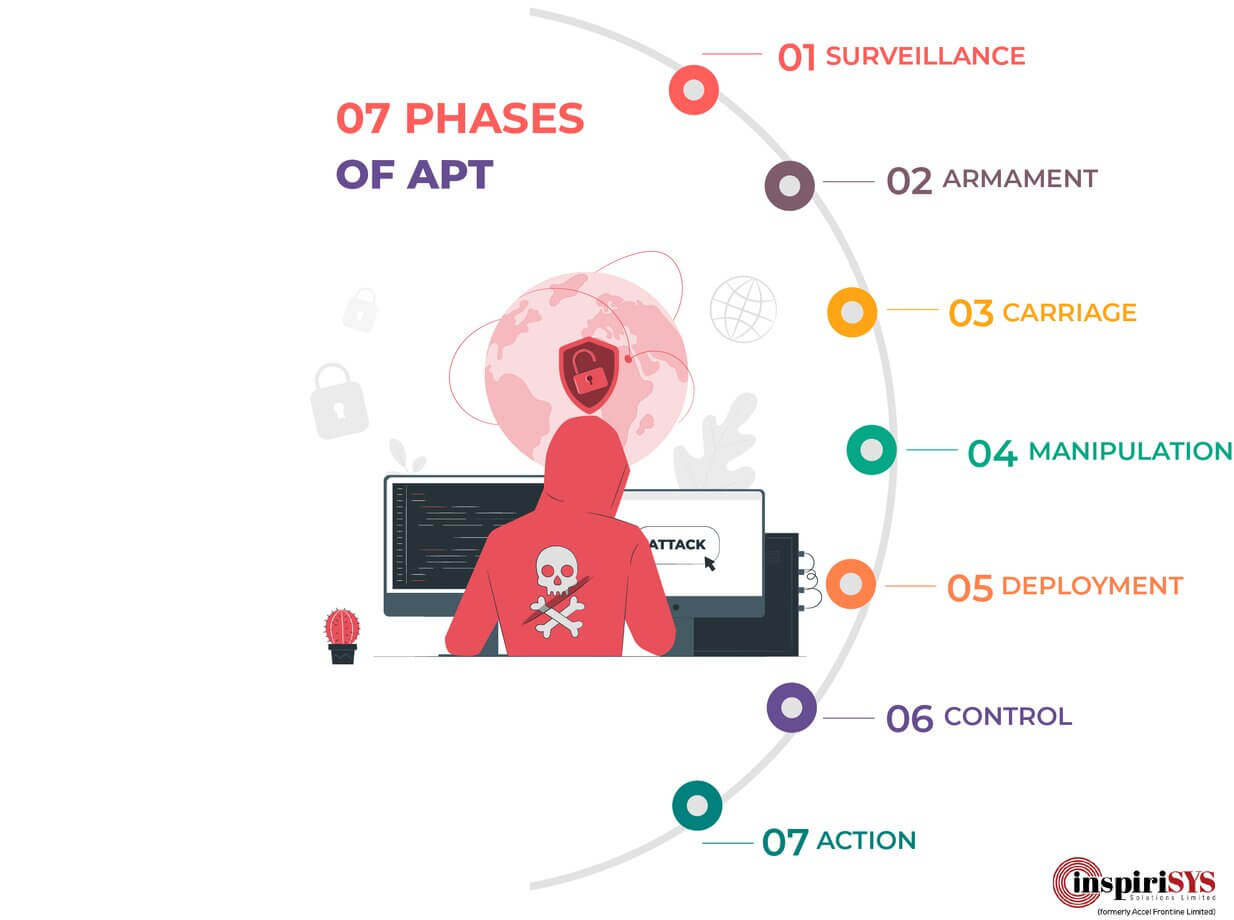
Phase 1: Surveillance
The intruder researches the victim to gain knowledge about vulnerability in the organization and the IT infrastructure. They crawl the web for potential email addresses or social media accounts like Facebook, Twitter, or LinkedIn etc. The attacker finds the right contact information to target by spear-phishing. Sometimes port scanning and social engineering techniques are used to gain a better perspective of who to attack.
Phase 2: Armament
The intruder builds a payload that can be transported to the targeted victim’s computer. Thus the vulnerability found in the Surveillance phrase is exploited with a Trojan packaged with a delivery system.
Phase 3: Carriage
The intruder finds means to deliver this weaponized payload to the victim’s computer. The three most prevalent forms of delivery are email, website and a USB stick. Now it is also evolved to cloud delivery. But email delivery or spear phishing is still the popular one with APTs.
Phase 4: Manipulation
The intruder triggers the execution of this weaponized payload. For instance, in email delivery, attachments like PDF or word documents are quite common. So the intruder exploits vulnerabilities in these files to trigger the execution of malicious code.
Phase 5: Deployment
The intruder gains easy access to the targeted victim’s system by deploying a malicious Trojan.
Phase 6: Control
After gaining the access, the payload initiates the connection with the intruder’s server, thereby making it easier for the intruder to shadow the compromised system and issue commands through the network. As most organisations employ firewalls to keep intruders at the bay by not letting them initiate communication with malware inside the network perimeter, the catch in hindering outbound communication means that most secured and reliable firewalls are less dependable and thus vulnerable to this form of attack.
Phase 7: Action
This is the final phase where the intruder has everything to exfiltrate the right confidential information, compromise data integrity or availability. The goal of intrusion may simply be to gain access to the secured system or network. But APTs can survey the system for weeks, months or even years to take small steps to accomplish the mission.
How Inspirisys can help your organization to defend against APT?
 Advanced Persistent Threats are distinctive because of the methodology they follow. They are advanced because unique malware is used based on the detailed knowledge of a specific IT environment and designed to bypass security infrastructure. Some organizations assume that APT only targets large-scale businesses. But it is not the reality. Whatever the size of the organization, APTs target and accomplish the goals. As an integral piece of an Adaptive Defence strategy, our state-of-the-art advanced persistent threat protection solutions protect against cyber-attacks with technologies such as
Advanced Persistent Threats are distinctive because of the methodology they follow. They are advanced because unique malware is used based on the detailed knowledge of a specific IT environment and designed to bypass security infrastructure. Some organizations assume that APT only targets large-scale businesses. But it is not the reality. Whatever the size of the organization, APTs target and accomplish the goals. As an integral piece of an Adaptive Defence strategy, our state-of-the-art advanced persistent threat protection solutions protect against cyber-attacks with technologies such as
- Firewall – First layer of defence against APT,
- Web Application Firewall – Monitor and block malicious web traffic.
- Antivirus – Detect and prevent a wide range of APT malware, Trojans and Viruses.
- Intrusion Prevention System – Detect malicious activity in the system and prevent any possible intrusion.
- Sandbox – Behaviour analysis to protect from APT
- Virtual Private Network – Encrypted connection to ensure sensitive data is safely transmitted.
- Advanced Email Protection – Scan and block APT malware in emails.
Our Anti-APT Solutions bolstered with advanced persistent tools reinforced to close the response gap by detecting malicious activities faster. Our Security Operations Center collects network data such as logs, packets, NetFlow and correlate with the advanced persistent threat intelligence engine to find malicious activities. We also provide smart analytics with automation capabilities to ease the process of threat hunting and to have 360-degree protection from advanced persistent threat groups.
Download 7 Phases of APT Infographic PDF