Quick Summary: In the digital landscape, where cyber threats are ever-evolving, Threat Detection and Response (TDR) is essential for safeguarding your organization. TDR uses advanced tools like machine learning and real-time monitoring to spot and stop cyberattacks early. By automating responses and alerting security teams, it helps prevent damage from threat actors, ensuring quick action to protect sensitive data and systems.
On average, cyberattacks occur every 39 seconds globally, putting your organization's data at constant risk. As the frequency of data breaches and ransomware attacks continues to rise, it's clear that traditional defenses like firewalls and antivirus software are no longer sufficient. Effective cybersecurity threat detection and response strategies are essential for safeguarding your assets. These strategies must be proactive, designed to identify and eliminate potential threats before they result in significant harm.
Consider the readiness of your organization: Is your security setup equipped to identify threats promptly? Are your systems capable of detecting malicious activity early enough to prevent damage? What measures are in place to handle a data breach that may go unnoticed for an extended period? The uncertainty around these questions underscores the critical importance of cybersecurity in today's digital landscape. This guide will delve into the significance of threat detection and response, providing insights into how to protect your organization against the ever-evolving cyber threats.
What is Threat Detection and Response?
Threat detection and response is the process of identifying any malicious actions that may threaten the network and then developing a suitable response to mitigate the threat before it exploits any vulnerability. In the context of an organization’s security program, “threat detection” encompasses multiple dimensions.
Even the best security programs need to be prepared for the worst-case scenarios, where threats have evaded defensive and preventive technologies. Detection and response require a collaboration between people and technology to manage such breaches. A comprehensive threat detection and response strategy combines people, processes and technology to detect signs of breaches and implement necessary actions.
What Are the Four Key Methods of Threat Detection?
Organizations use various techniques to identify and address potential cybersecurity threats. These techniques can be grouped into four main categories:
1. Signature-Based Detection
This method involves comparing network traffic or data patterns against a predefined database of known attack signatures. It is highly effective for recognizing familiar threats like specific malware strains. However, it struggles with detecting newer, polymorphic threats that don’t match existing patterns.
2. Anomaly-Based Detection
This approach identifies unusual activities or deviations from established baseline behaviors within an IT environment. While effective in uncovering insider threats, zero-day exploits, and other previously unknown risks, it can sometimes produce false positives, especially in complex and evolving environments.
3. Behavior-Based Detection
Advanced analysis of user, application, and system behaviors helps uncover threats like privilege escalation, lateral movement, and data exfiltration. The approach relies on advanced analytics and a deep understanding of normal operations to detect these hidden dangers.
4. Threat Intelligence-Based Detection
External data sources provide the foundation for threat identification, and in this technique, the focus remains on indicators like malicious IP addresses, domains, and file hashes. Alert enrichment with actionable intelligence enables proactive threat prevention and strengthens the impact of other detection techniques.
How Does Threat Detection and Response Work?
Threat Detection and Response (TDR) systems are vital tools in cybersecurity, equipped with advanced features designed to proactively detect and respond to cyber threats. Here's how these systems operate:
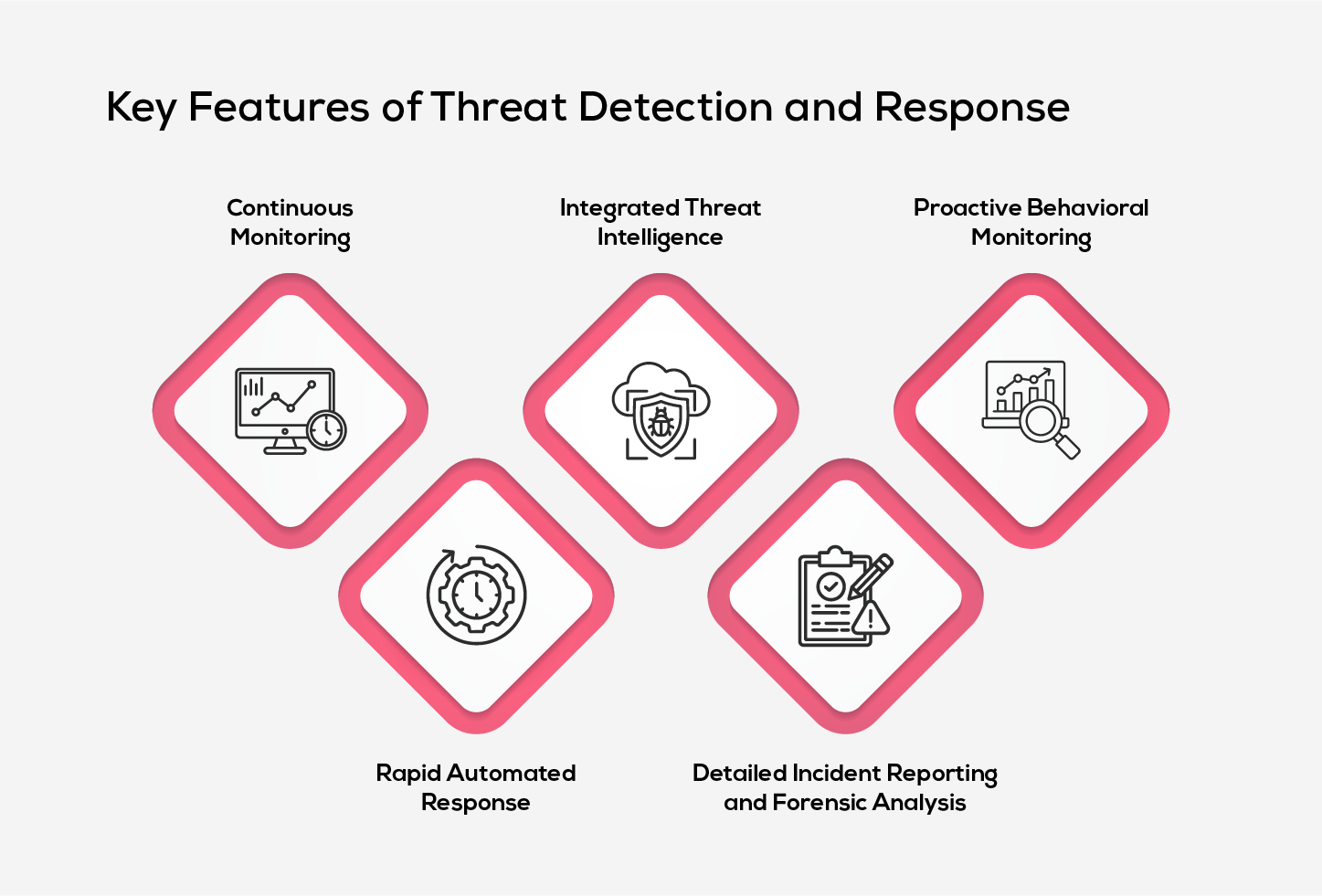
1. Continuous Monitoring
Monitoring networks, solutions and endpoints in real-time, TDR solutions maintain relentless surveillance to ensure that no potential risk is neglected. This thorough approach enables organizations to detect suspicious activities and provide a complete view of the infrastructure, serving as the primary defence against unusual access behaviours.
2. Integrated Threat Intelligence
Global threat intelligence feeds that are constantly updated with the latest information on emerging threats, vulnerabilities and cybercriminal tactics, are seamlessly integrated into TDR systems. This crucial integration allows the systems’ monitoring capabilities for malware signatures and phishing attacks, keeping organizations informed about the threats.
3. Proactive Behavioral Monitoring
TDR solutions employ behavioural analysis to spot actions violating typical system behaviour, which may indicate a security threat. By stablishing a baseline of normal activities like login patterns and resource utilization, these systems can quickly detect any irregular actions and enhance security measures.
4. Rapid Automated Response
Equipped with automated detection and response capabilities, TDR systems swiftly neutralize detected threats. Immediate actions such as blocking certain IP addresses, shutting down infected processes and isolating compromised devices help minimize the attack surface and potential impacts.
5. Detailed Incident Reporting and Forensic Analysis
Upon detecting a security breach, TDR systems generate instant detailed incident response and forensic insights, allowing security teams to understand the attacker’s scope and nature. These reports provide a comprehensive timeline, and outline measures taken for mitigation, which are essential for both post-incident and regulatory compliance, so that organizations act effectively.
Key Threats Identified by TDR
TDR solutions are structured to provide strong protection against a wide range of cyber threats. By leveraging advanced technologies, these systems enable organizations to detect and neutralize risks efficiently. Below are the specific types of threats that TDR can identify and prevent:
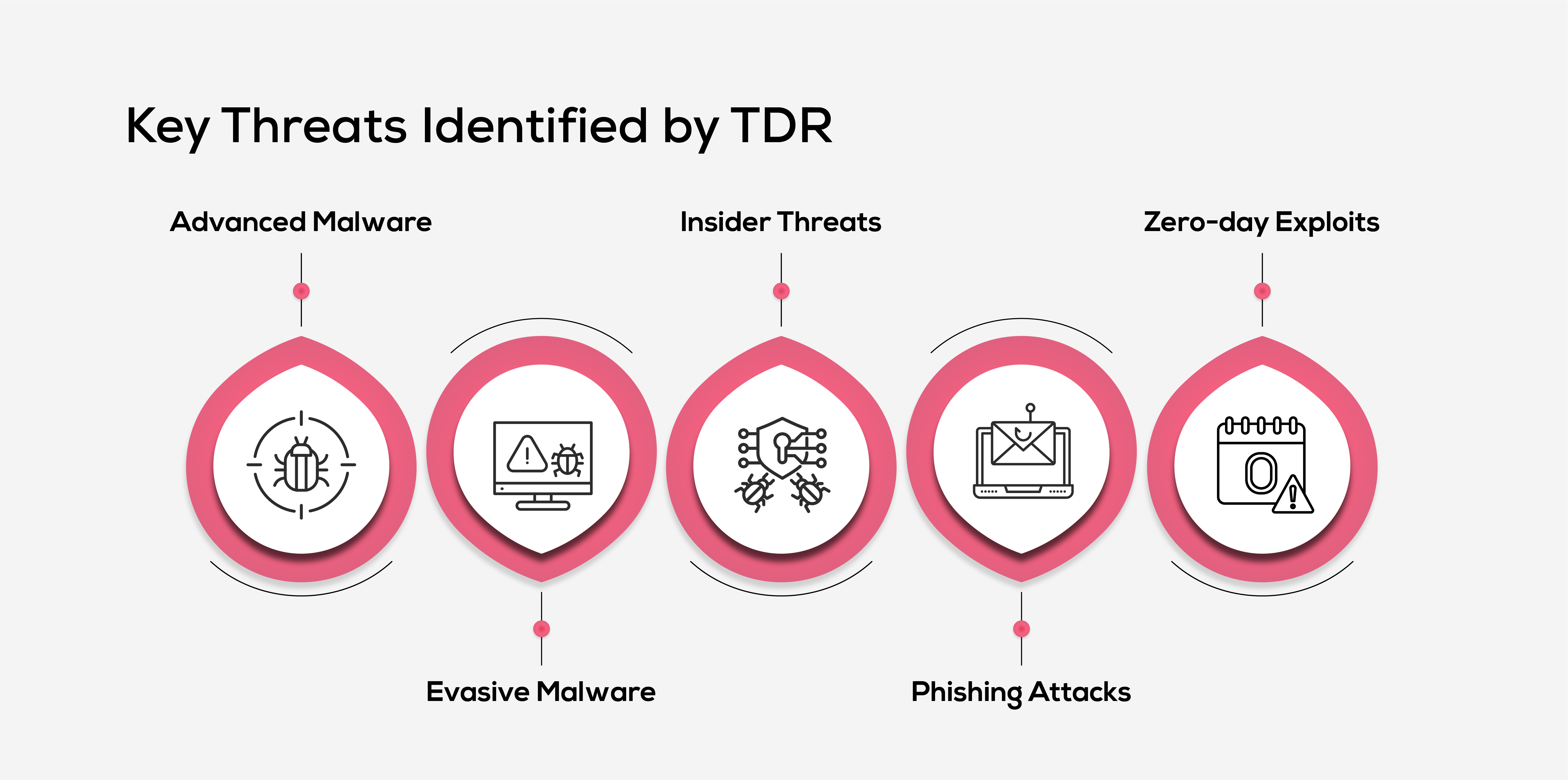
1. Advanced Malware
Malware, including viruses, ransomware, and trojans, is a persistent threat to organizations. Modern malware often employs techniques like polymorphism to evade signature-based detection by constantly altering its identifiable features. TDR solutions analyze behavioral patterns and monitor for irregular system activities to identify and neutralize these threats before they can cause downtime or compliance violations.
2. Evasive Malware
Some malware uses advanced tactics such as sandbox evasion, process injection, and obfuscation to bypass traditional security tools. By staying undetected for longer periods, this type of malware increases the damage it can cause, including breaches and reputational harm. TDR systems address this by leveraging anomaly detection and machine learning to uncover hidden threats and act swiftly to mitigate them.
3. Insider Threats
Not all threats come from external sources. Insider threats, whether intentional or accidental, can significantly pose serious risks to an organization. These threats often stem from unauthorized access to sensitive data or unusual file transfers by employees or compromised accounts. TDR systems continuously monitor user activities to detect irregular behaviors and prevent insider threats from escalating into major breaches.
4. Phishing Attacks
Cybercriminals frequently use Phishing as a common tactic to steal login credentials and financial data. TDR system effectively analyzes email content, links and attachments against known indicators of compromise (IoCs) to identify and neutralize phishing attempts. This prevents employees from falling victim to fraudulent communications, helping organizations safeguard sensitive information.
5. Zero-day Exploits
Zero-day exploits target software vulnerabilities that are unknown to developers, posing significant risks by exploiting security weaknesses that organizations are yet to identify. TDR solutions mitigate these threats by analysing behavioural patterns and system changes and alerting security teams to respond promptly even before the official patches are released.
Essential TDR Tools and Solutions
Having the right combination of tools and solutions is essential to quickly detect and respond to cybersecurity threats that cannot always be fully prevented. Tools are specialized technologies designed to perform specific functions, while solutions bring together various capabilities into unified frameworks, enhancing an organization’s overall security posture.
- SIEM Systems
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems gather and centralize log data from various sources across cloud platforms and networks. These logs are then analyzed to uncover potential threats, giving security teams the insights needed to act.
- IDS and IPS
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns, while Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) go a step further by blocking harmful data packets to prevent attacks before they escalate.
- EDR Systems
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions focus on safeguarding endpoints such as user devices and applications. Using AI and sandboxing, they identify malware and counter advanced evasion techniques to protect against endpoint-targeted threats.
- UEBA Tools
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) solutions use machine learning to track and analyze activity patterns across users, devices, and systems. Unusual behaviors are flagged as potential threats, enabling quick investigation and response.
- CASB
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB) act as gatekeepers between users and cloud applications. They enforce security policies, monitor cloud usage, and extend on-premises security practices to cloud environments, safeguarding organizational data.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms
These platforms give organizations a detailed view of potential attack vectors, including email systems, networks, and cloud environments. By integrating real-time threat insights, they enable proactive monitoring of ongoing risks.
- Advanced Data Analytics
Data analytics solutions simplify threat management by processing large volumes of data and filtering out false positives. This ensures security teams can focus their efforts on addressing real, high-priority risks.
- Integrated Threat Intelligence Feeds
Real-time intelligence feeds deliver updates on evolving cyber threats. These feeds are used by tools such as SIEM and EDR to identify and classify risks, ensuring organizations stay ahead of emerging challenges.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a TDR Solution
Selecting the right Threat Detection and Response solution is a critical decision for organization aiming to enhance their cybersecurity posture. With numerous TDR offerings from various sectors, it is important to evaluate the options to that align with the organization’s goals and needs.
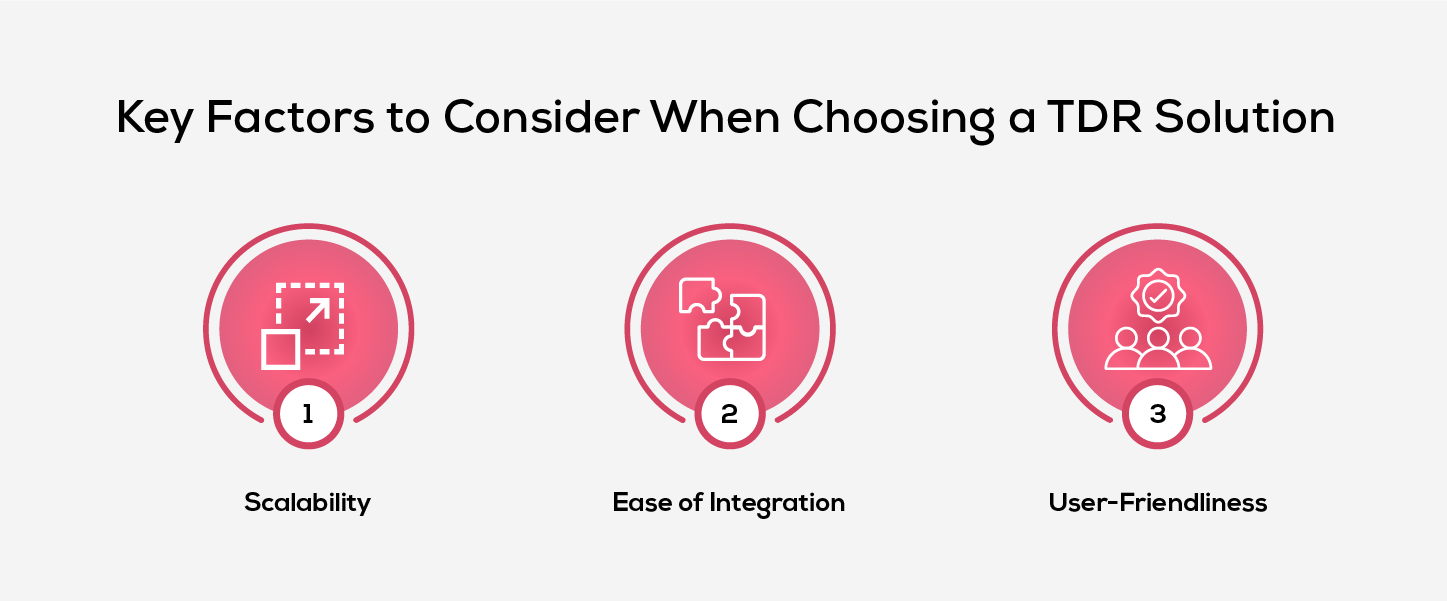
1. Scalability
A good TDR solution should scale with your organization. As business requirements and threat landscape evolve, the solution must adapt to handle larger data volumes, integrate new technologies and the expand to cover growing network environments. This adaptability helps the organization remain protected as its security demands change.
2. Ease of Integration
It’s essential to ensure that the TDR solutions easily integrate with the current organization tools and infrastructure, such as firewalls, endpoint protection systems and intrusion detection tools. This capability ensures that organizations can maximize the effectiveness of security operations without unnecessary complexity.
3. User-Friendliness
A user-friendly TDR system simplifies deployment and usage, making it easier for security teams to adopt and use effectively. Features like an intuitive dashboard, easy report generation, and straightforward navigation enable quicker decision-making during security incidents, ensuring smoother operations.
Conclusion
Threat Detection and Response (TDR) solutions are critical for organizations to detect and address evolving cyber threats effectively. By utilizing advanced technologies like machine learning and behavioral analytics, these solutions improve visibility, automate routine tasks, and simplify operations to reduce risks and costs.
In addition to adopting TDR solutions, organizations should prioritize educating employees on cybersecurity practices. Regular training sessions on recognizing phishing attempts, creating strong passwords, and following security guidelines help build a security-conscious culture, strengthening the organization’s defenses.
This comprehensive approach provides resilience against emerging threats while protecting critical assets and reputation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is false positive?
A false positive refers to a situation where a detection tool incorrectly flags a non-existent threat or vulnerability. This misidentification leads to unnecessary alerts and forces IT resources to investigate non-existent problems, ultimately slowing down efficiency and impacting the productivity of security teams.
2. What is the difference between EDR and TDR?
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) focuses on detecting and mitigating threats at endpoints like devices and servers. Threat Detection and Response (TDR) provides broader security, monitoring the entire network, including endpoints, cloud systems, and more, for comprehensive threat detection and response.
3. How does behavioural analysis help in threat detection?
Behavioral analysis tracks the activities of users and systems to determine what constitutes normal behavior. It subsequently monitors for any deviations from this baseline, such as unusual login locations or unexpected file access, which could indicate a possible security threat.
4. How often should the system be updated?
Systems should be updated as soon as manufacturers release new updates. These updates often include security patches to fix vulnerabilities, new security features, and performance improvements. While many updates are automatic, some may require manual installation to stay protected.
5. Can threat detection systems identify insider threats?
Yes, modern threat detection tools can monitor user behavior and access to sensitive data, helping to spot unusual actions by trusted insiders or compromised accounts, which aids in mitigating insider threats.







