Quick Summary: Undertaking a Core Banking System (CBS) transformation is a complex endeavour that demands strategic foresight. This article outlines key mistakes to avoid during the transition, offering insights to help banks navigate the challenges of people, processes, and technology for a successful outcome.
In the rapidly evolving financial industry, core banking transformation is no longer just an option—it's a necessity for survival. As the financial landscape undergoes dramatic shifts driven by digital innovation and increased competition, institutions must adapt or risk becoming obsolete. The pressure to stay relevant has never been greater, and the quest for the perfect core banking solution has become central to navigating this turbulent environment.
With a myriad of core banking solutions promising to revolutionize operations, financial institutions face the daunting task of choosing the right one. The stakes are high: selecting an inadequate solution can lead to operational inefficiencies, compliance issues, and a diminished customer expectations—factors that can erode an institution’s reputation and bottom line.
To steer clear of these pitfalls, a strategic approach to core banking transformation is essential. To navigate this complex terrain successfully, you need more than just a good solution—you need a well-rounded strategy. In this article, we’ll dive into the essential pillars of core banking transformation: understanding the importance of data migration, crafting a robust core banking data migration strategy, and pinpointing the mistakes to avoid to ensure a smooth and successful transition. Let’s chart a course for success and eliminate the common pitfalls that can derail your transformation journey.
What is Data Migration?
Data migration is a vital process for banks and financial institutions involving the transfer of data from legacy systems to modern core banking platforms. As technology evolves, banks must upgrade their systems to stay competitive. This migration ensures that important information is accurately, consistently, and securely transferred, preventing data loss or corruption during the switch.
Role of Data Migration in the Banking Industry
In banking, trust is everything. Technology drives every aspect of financial services today, from personalized customer experiences to efficient operations. As banks adopt new core banking solutions, data migration becomes crucial for a smooth transition. The aim is to transfer customer data and records seamlessly across systems, enhancing efficiency, improving operational efficiency, and managing costs effectively.
However, data migration can be complex. Data is often spread across different systems, which makes the migration process challenging. To ensure success, banks must approach data migration strategically, considering their unique needs, future plans, and regulatory requirements.
Here are some key reasons why data migration is critical in the banking sector:
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Combining data from multiple sources to create a unified system.
- Replacing Old Systems: Ensuring data is transferred without loss when switching from outdated technology.
- Regulatory Compliance: Maintaining accurate and consistent data for legal and reporting purposes.
- Improving Data Quality: Cleaning and consolidating data for better accuracy and readability.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Providing a seamless experience across all banking channels.
- Business Continuity: Enabling quick data recovery to ensure uninterrupted operations in case of emergencies.
Core Banking Data Migration Strategy
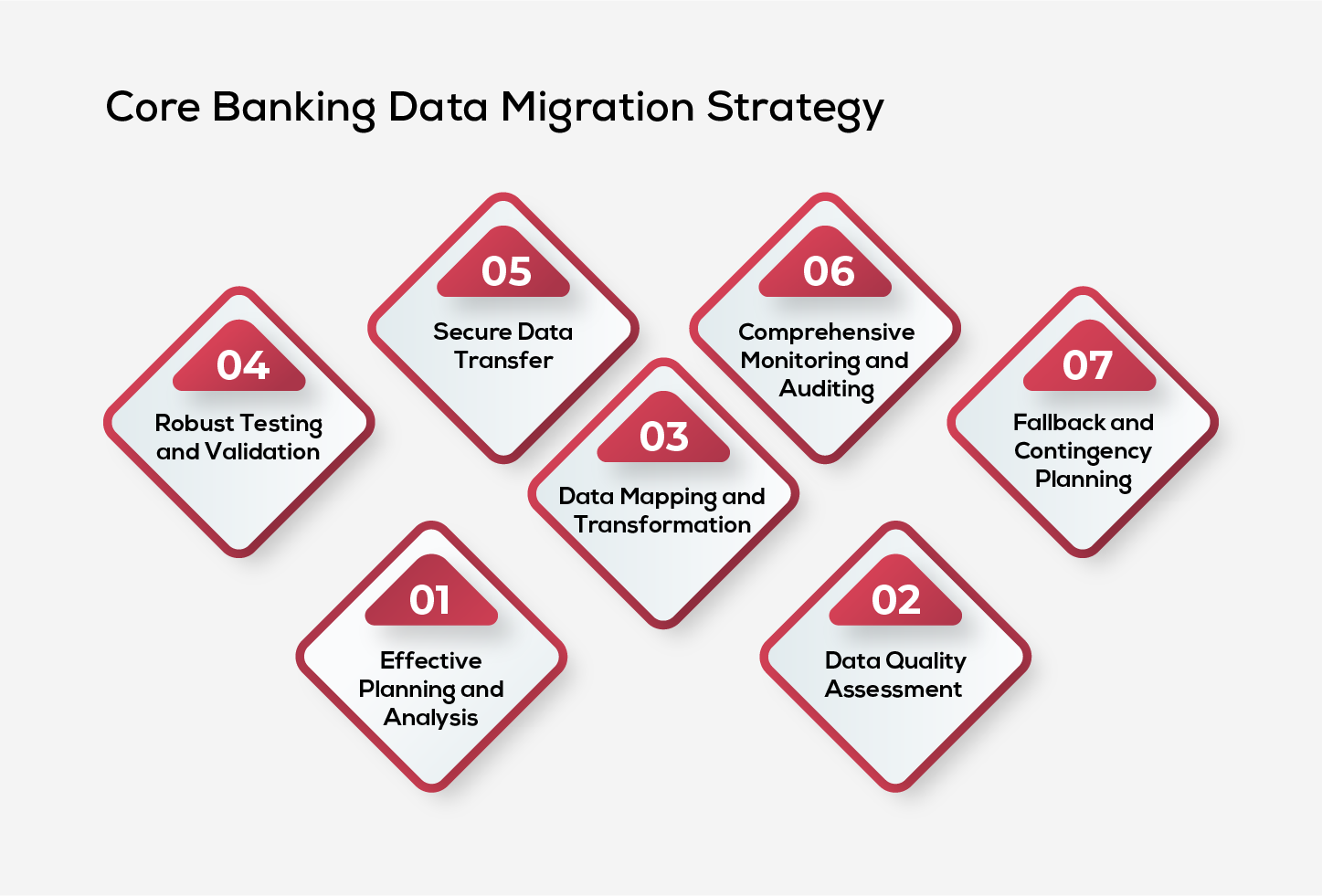
For a successful core banking data migration, crafting a thoughtful and organized strategy is key. This plan should integrate various best practices to navigate the complexities of data transfer effectively. We’ll outline the crucial strategies to guide you through this intricate process smoothly.
-
Effective Planning and Analysis
- Review the existing data landscape, including data sources and formats.
- Identify and prioritize critical data elements based on business needs and regulatory requirements to deliver a smooth migration.
-
Data Quality Assessment
- Check the quality of source data and address any issues before migration.
- Ensure the data is accurate, consistent, and complete to maintain its integrity.
-
Data Mapping and Transformation
- Create a detailed plan to align the old data structures with the new system’s data models.
- Identify any necessary data transformations, such as format changes or data enrichment.
-
Robust Testing and Validation
- Implement thorough testing procedures to verify the accuracy and completeness of the migrated data.
- Use test cases and data sampling to ensure the migrated data matches the source data.
-
Secure Data Transfer
- Use secure methods to transfer data, protecting sensitive customer and financial information.
- Ensure data is encrypted during transfer and storage, with strict access controls.
-
Comprehensive Monitoring and Auditing
- Monitor the data migration process and keep a detailed record of progress.
- Track any issues or errors and maintain a comprehensive audit trail for compliance and future reference.
-
Fallback and Contingency Strategies
- Prepare a backup plan to address any unexpected problems during migration.
- Include detailed procedures for data recovery and rollback to achieve a smooth recovery in case of issues.
By following these practices, financial institutions can ensure a smooth and successful core banking transformation, supporting their strategic goals and operational needs.
Mistakes to Avoid When Changing Your Core Banking Platform
As financial institutions embark on core banking transformation, understanding and avoiding common pitfalls is essential for a successful transition. Here are the key mistakes to avoid for a successful implementation of core banking:
1. Inadequate Planning and Analysis:
- Mistake: Rushing into migration without thorough planning and analysis can lead to unexpected issues. Financial institutions may overlook critical data elements or fail to align their strategy with business needs.
- Solution: Conduct comprehensive planning and analysis. Review existing data landscapes, prioritize critical data, and ensure alignment with regulatory requirements, as well as strategic and operational goals to promote a smooth transition.
2. Overlooking Data Quality:
- Mistake: Neglecting data quality assessment can result in transferring inaccurate, inconsistent, or incomplete data, leading to operational inefficiencies and regulatory compliance issues.
- Solution: Conduct a rigorous data quality assessment before migration. Cleanse, validate and consolidate data to enhance its overall quality, ensuring accuracy and consistency in the new system.
3. Insufficient Testing and Validation:
- Mistake: Failing to implement robust testing and validation procedures can lead to errors and discrepancies in the migrated data, impacting functionality and user experience.
- Solution: Develop a comprehensive testing and validation plan. Use test cases and data sampling to verify the data accuracy, ensuring the migrated data aligns with the source and the new system functions as intended.
4. Ignoring Secure Data Transfer:
- Mistake: Using insecure methods for data transfer can expose sensitive customer and financial information to risks, including data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Solution: Employ secure data transfer methods, including encryption during both transmission and storage. Implement strict access controls to protect sensitive information throughout the migration process.
5. Lack of Monitoring and Contingency Planning:
- Mistake: Failing to monitor the migration process and prepare for contingencies can result in unmanaged issues and prolonged system disruptions.
- Solution: Establish a monitoring and auditing framework to track progress and address any issues promptly. Develop a fallback and contingency plan to handle unexpected problems, ensuring quick data recovery and system stability.
By avoiding these common mistakes and adhering to best practices, financial institutions can achieve a successful core banking transformation, enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The Five Pillars of Core Banking Solution
Core banking solutions are built on five essential pillars that ensure their effectiveness and sustainability. These pillars are foundational to enhancing operational efficiency but also align with fundamental banking principles:
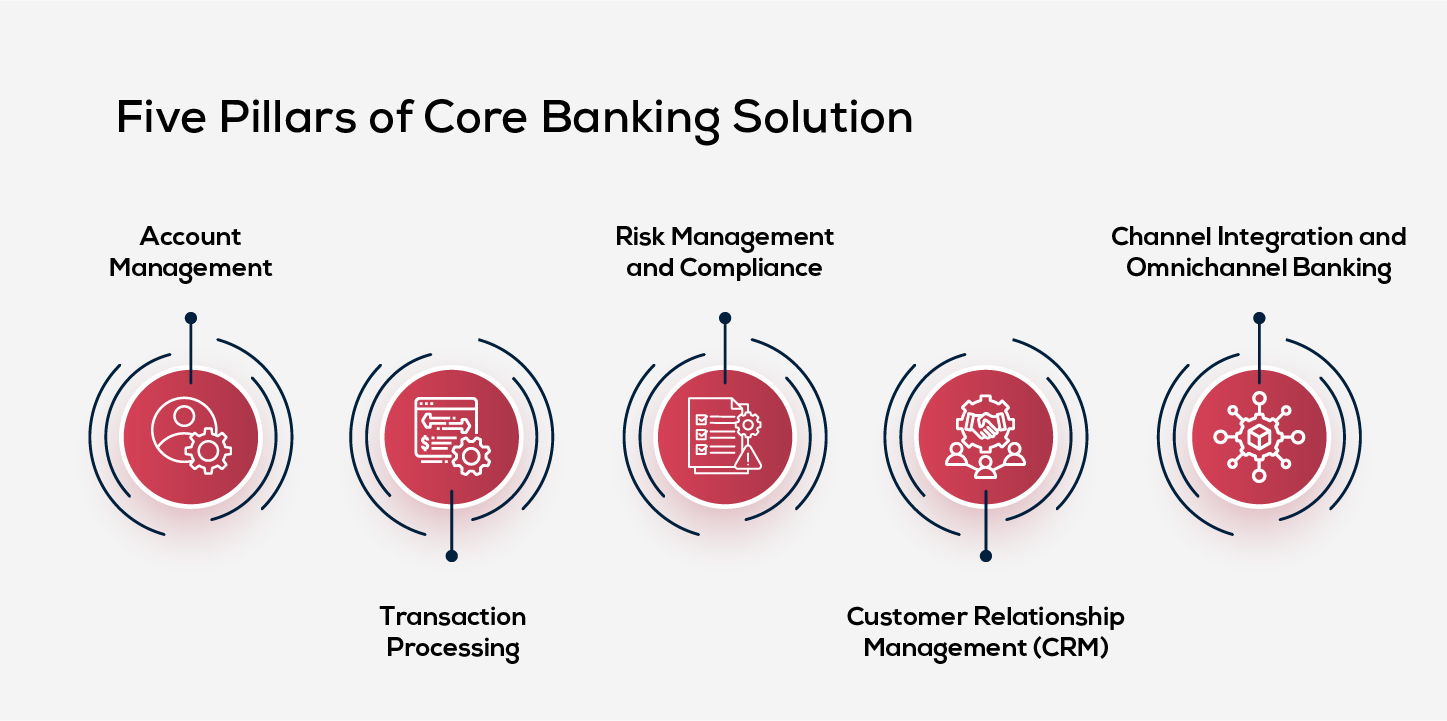
1. Account Management
Account management facilitates the role of banks as intermediaries, efficiently managing customer accounts such as savings, loans, and deposits. Effective account management enables banks to process transactions accurately, provide timely customer support and establish strong relationships based on high customer satisfaction.
2. Transaction Processing
Transaction processing is crucial for core banking operations for maintaining liquidity, providing real-time processing of payments, fund transfers, and reconciliations. This ensures banks have the necessary cash flow to meet operational needs and customer demands.
3. Risk Management and Compliance
Robust risk management and compliance systems build trust by ensuring the security of assets, regulatory adherence and effective risk mitigation. This helps banks strengthen customer and stakeholder confidence.
4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM tools enhance profitability by improving customer engagement and satisfaction. By analyzing customer data and preferences, banks can tailor their offerings, identify cross-selling opportunities, and drive revenue growth, contributing to improved profit.
5. Channel Integration and Omnichannel Banking
Omnichannel banking ensures seamless integration across multiple touchpoints, supporting accurate financial reporting and liquidity management, which are key to maintaining solvency and financial stability.
These pillars, when combined with core banking principles, assure that banks operate efficiently, maintain trust, and achieve long-term success in a competitive and dynamic environment.
How to Select the Right Core Banking Solution for Your Organization
Choosing the right core banking solution (CBS) is crucial for your organization’s success. It involves considering several key factors to ensure the solution meets your current needs and future growth.
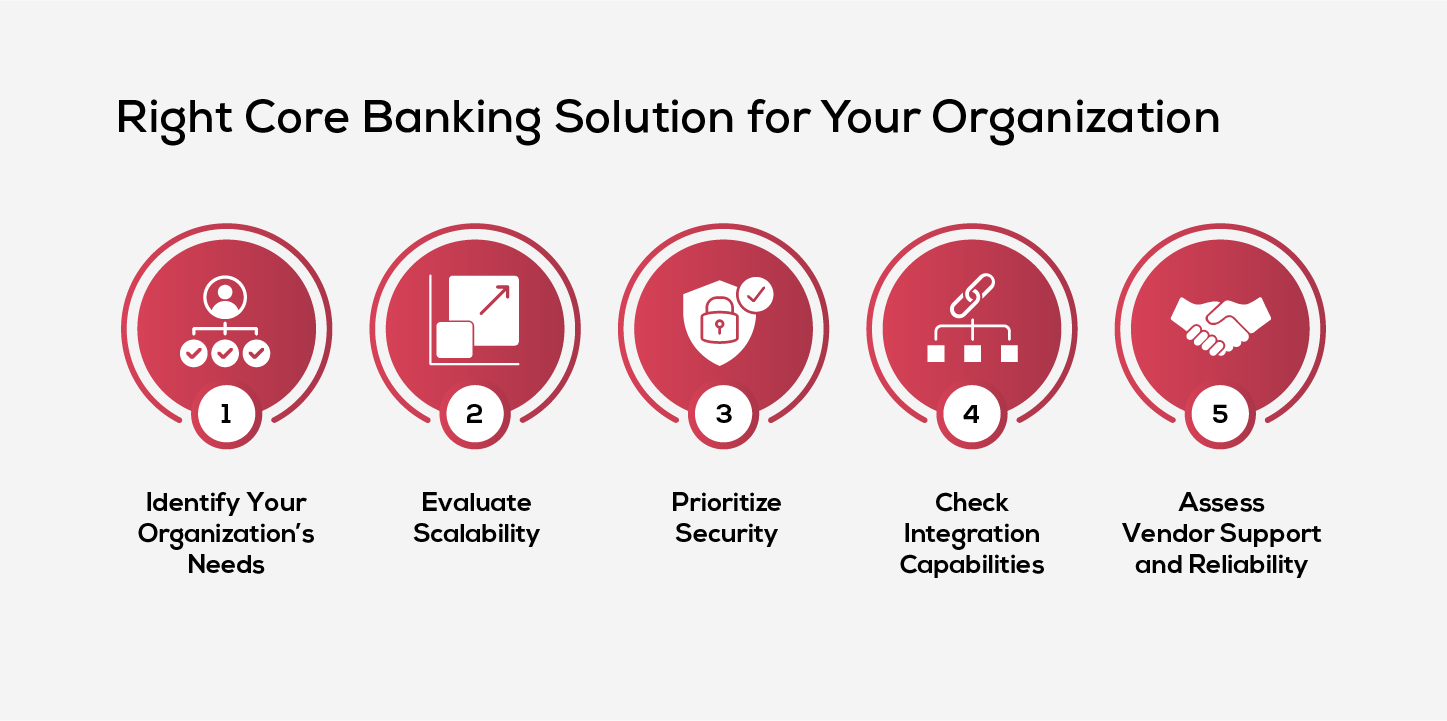
1. Identify Your Organization’s Needs
Begin by assessing your organization’s specific requirements. What are your current challenges and goals? Whether you’re looking to enhance customer experience, expand your offerings, or streamline operations, understanding these needs is essential. Consider the aspects such as the types of accounts you offer, transaction volumes, regulatory requirements, and the need for real-time processing and risk management. Engage key stakeholders like IT staff, executives, and frontline employees to ensure a thorough assessment of your needs.
2. Evaluate Scalability
Scalability is vital for long-term success. As your organization grows, your CBS should be able to handle more transactions, accounts, and complex banking products without increasing operational costs or complexity. The system should also adjust during periods of lower demand, ensuring your investment continues to support growth over time.
3. Prioritize Security
Security is a top priority in banking. Your CBS must have strong security measures to protect sensitive customer data and financial transactions. Data encryption, secure user authentication, and regular security updates are all included in this. Ensure the system complies with industry regulations and verify that the vendor has a solid track record in managing security risks effectively.
4. Check Integration Capabilities
CBS must integrate smoothly with other systems, including existing IT infrastructure, digital platforms, and payment gateways. Look for a solution that offers flexible integration options through APIs, ensuring seamless operation within your current technology ecosystem.
5. Assess Vendor Support and Reliability
The vendor’s support and reliability are crucial to the success of your CBS. They should offer robust support during implementation and ongoing maintenance. Evaluate their history in system uptime, issue resolution, and customer satisfaction. Additionally, consider the vendor’s financial stability and commitment to continuous improvement, as they will be a key partner in your organization’s digital transformation journey.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a core banking solution that not only meets your immediate needs but also supports your organization’s long-term success.
User Expectations from Modern Core Banking Systems
In the rapidly changing financial landscape, users' demands from core banking systems have grown significantly. To stay competitive, banks must adapt to these evolving expectations, which include a range of key requirements. These expectations are outlined as follows:
Beyond Traditional Banking
Today’s users demand more than just traditional banks. They expect a suite of financial tools at their fingertips—think budgeting assistance, investment opportunities, and seamless integration with third-party financial apps. The great news? Modern core banking systems are designed to effortlessly connect with these services, meeting users' evolving expectations.
The Power of Personalization
In an era where personalization is key, users expect their banks to know and cater to their unique financial needs. With advanced core banking systems, banks can deliver tailored financial products and services, enhancing user satisfaction and loyalty.
Speed is Everything
Gone are the days when users were content with waiting for transaction updates. Now, they demand real-time processing, instant notifications, and swift updates. Core banking systems must be equipped to meet these expectations, ensuring that every transaction is handled quickly and efficiently.
AI-Driven Assistance
Incorporating AI chatbots or virtual assistants into the core banking system can significantly elevate the user experience. These intelligent tools provide immediate responses to basic queries, resolve simple issues, and even offer personalized recommendations—all in real-time, improving customer engagement and satisfaction.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of a core banking system transformation requires more than just technical upgrades; it demands careful planning, stakeholder alignment, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By avoiding common mistakes such as underestimating the scope, neglecting stakeholder engagement, and overlooking data migration, banks can significantly reduce the risk of delays and cost overruns. A proactive approach, which includes regularly revisiting strategies in people, processes, and technology, not only ensures the success of the current transformation but also equips the organization to handle future challenges with greater agility. Ultimately, the banks that embrace these best practices will emerge stronger, with a robust and future-ready core banking system that supports their long-term strategic goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is core banking solution?
A Core Banking Solution (CBS) is a software platform that banks use to manage their main operations. It allows customers to perform transactions at any branch, not just the one where they opened their account. CBS systems handle activities like managing accounts, loans, and payments, and they keep customer information updated in real-time.
2. What are the components of Core Banking System?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Account Management, Risk & Compliance Management, Payment and Transaction Processing and Loan Disbursal & Management.
3. What are some of the top core banking software?
Finacle, Temenos, Mambu, Backbase, Finastra, Oracle FLEXCUBE, etc are some of the best software for core banking.
4. What is the architecture of a Core Banking Solution?
The architecture of a Core Banking Solution typically includes layers for user interface, business logic, data management, and security. It enables seamless integration, real-time processing, and secure operations across various banking functions.
5. What is the RBI's Core Banking Solution?
The Reserve Bank of India's core banking solution, known as E-kuber enables commercial banks to access their current accounts with the RBI anytime, from anywhere.