Quick Summary: Robust cybersecurity is crucial to safeguarding sensitive data and systems from evolving threats. This article highlights essential tools and strategies to help organizations stay ahead of cyber risks.
Cybersecurity tools are critical in an era dominated by digital transactions, where the importance of robust cybersecurity measures cannot be overstated. Businesses of all sizes are continually at risk from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats that target sensitive data and disrupt operations. Highlighting the significance and escalating reliance on these tools, recent market analysis provides insightful data.
According to Gartner, global end-user spending on information security is expected to reach $212 billion in 2025, marking a 15.1% increase from $183.9 billion in 2024. This surge highlights the rising commitment of organizations to fortify their cybersecurity defenses amid an increasingly complex threat landscape.
However, it is not necessary to operate in the shadow of these threats. This article will enumerate essential tools that every organization requires to fortify their digital defenses and preserve operational integrity.
What are Cybersecurity Tools?
Cybersecurity tools are the backbone of online security, helping detect, analyze, and remediate vulnerabilities while safeguarding privacy and endpoint security. They defend against existing threats, identify emerging risks, and mitigate future damage. Proper implementation ensures digital asset integrity and fosters trust in an increasingly connected world. With evolving cyber threats, businesses must proactively monitor their IT environment and adapt to new security challenges.
Types of Cybersecurity Tools
Cybersecurity encompasses a variety of tools, each designed to tackle specific security challenges. From firewalls that guard network perimeters to encryption tools that protect data confidentiality, the range of tools available is tailored to enhance organizational security across multiple vectors.
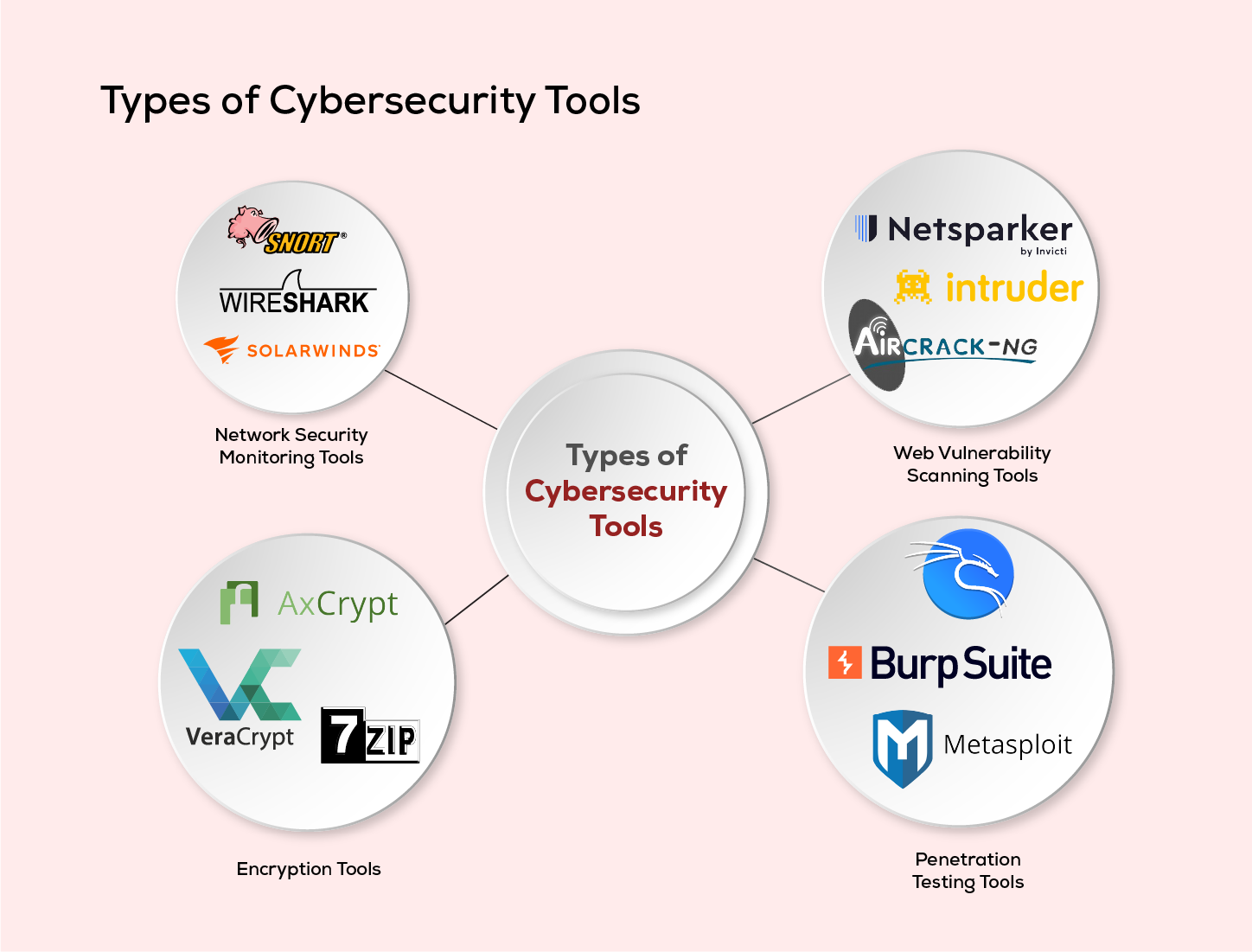
1. Network Security Monitoring Tools
Network Security Monitoring (NSM) tools prioritize security over traditional network monitoring focused on performance. By employing software and hardware solutions for real-time traffic analysis and intrusion detection, NSM tools enable proactive threat response and restrict unauthorized access. These tools effectively monitor encrypted traffic and key network metrics to maintain robust network health and security.
Learn more about these tools below:
-
SolarWinds
SolarWinds provides a range of network management and monitoring solutions, including specialized tools for network security monitoring. These tools are capable of detecting modifications in security policies and traffic patterns, which enables swift and effective responses. Known for its robustness and popularity, SolarWinds quickly diagnoses and resolves network performance problems and outages with maximum efficiency.
Key Features:
- Multi-vendor network monitoring
- Smart visual mappings
- Advanced alerting capabilities
Benefits:
- Provides an intuitive interface, making it accessible for both novice and seasoned IT professionals.
- Delivers immediate insights into network health, performance, and security with excellent real-time monitoring.
- Simplifies compliance with automated, detailed reporting that meets industry and regulatory standards.
- Enables thorough analysis of historical data to help identify and mitigate future network vulnerabilities.
Limitations:
- It requires a significant initial investment and ongoing costs as network needs expand.
- The setup process is time-consuming and prone to errors, complicating installation.
-
Snort
Snort is an open-source Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) that employs a rule-based approach to identify malicious activities and generate security alerts to users. Its adaptability in deployment and flexibility across various operational modes like Sniffer mode, Packet logger mode, Network Intrusion Detection System mode, render it ideal for both personal and professional settings, meeting diverse network security demands.
Key Features:
- Network Traffic Logging
- Threat Detection and Alerts
- Protocol Analysis for HTTP & FTP
Benefits:
- Allows for the storage of packet data in files, facilitating detailed analysis with other tools.
- Automates remediation actions upon detection of intruders, enhancing security responsiveness
- Offers extensive customization options through adaptable rulesets, allowing for tailored security configurations.
Limitations:
- The setup process and configurations can be complicated for beginners, posing a steep learning curve.
- There is a lack of proper backend support, which may affect troubleshooting and maintenance.
-
Wireshark
Wireshark is an open-source packet analyzer offering wide-ranging tools for real-time monitoring, analysis and visualization of network traffic. It can analyze hundreds of network protocols and provides detailed status reports. As a packet browser, it is also capable of offline use. Wireshark reads data from numerous technologies including Ethernet, Bluetooth, PPP/HDLC, IEEE 802.11, ATM, USB, and more. Its compatibility with multiple operating systems like Windows, macOS, Linux, Solaris, NetBSD, and FreeBSD adds to its broad appeal.
Key Features:
- Packet Sniffing tool to capture live data packets
- Packet Analyzer tools for protocol Analyses
- Precise network filtering
Benefits:
- Provides a user-friendly interface.
- Allows detailed observation of network traffic, aiding in troubleshooting and detailed investigation of activities.
- Supports a broad range of protocols, enhancing its versatility in analyzing different types of network traffic.
Limitations:
- Lacks significant networking knowledge, presenting a high learning curve that may deter beginners.
- Less suitable for real-time monitoring of large networks that need automated analysis.
2. Web Vulnerability Scanning Tools
Web vulnerability scanners are critical tools for uncovering security risks in web applications. By systematically testing for a range of vulnerabilities, including Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), SQL Injection, and Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF), these tools provide an essential defense mechanism.
Let's explore these tools in depth to better grasp their protective capabilities.
-
Netsparker
Netsparker, a web application vulnerability scanner has an advanced automation feature that transforms the process of identifying security vulnerabilities. This popular tool offers a wide range of advanced features to help identify and improve security vulnerabilities in web applications. One of its key strengths is its crawling technology, which enables it to explore and analyze web applications to discover potential security risks.
Key Features:
- Accurate vulnerability detection
- Seamless tool integration
- Offers a proof-based scanning approach
Benefits:
- Supports Quick Deployment with minimal configuration and setup effort.
- Reduces False Positives for more accurate threat detection.
- Facilitates DevOps Integration for smooth automation and collaboration.
Limitations:
- Costs More compared to other cybersecurity solutions.
- Lacks Flexible Pricing with limited plan options available.
-
Intruder
This popular tool is designed to identify vulnerabilities such as missing security patches, web application attacks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and CSRF, as well as applications set with default passwords. It categorizes and prioritizes these vulnerabilities based on their cyber risks, ensuring that the most critical issues are addressed first. Available as a commercial product, it offers three versions: Pro, Essential, and Verified.
Key Features:
- Automated Vulnerability Scanning
- Comprehensive Coverage of servers, websites, and cloud environments.
- Detailed Security Reporting
Benefits:
- Integrates Seamlessly with AWS, Azure, Cloudflare, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Simplifies Operations with its intuitive and user-friendly interface.
- Provides Continuous Support with 24/7 customer service availability.
Limitations:
- Excessively burdensome for smaller organizations due to its high pricing.
- Frequently generates false alarms, leading to inefficiencies in threat response.
-
Aircrack
Aircrack stands out for its ability to detect vulnerabilities, especially in Wi-Fi network security assessments. It supports a broad array of operating systems including Solaris, NetBSD, Windows, and others, showcasing its adaptability. The tool provides a comprehensive framework that enables the identification and exploitation of weaknesses in wireless networks, making it an excellent choice for organizations with diverse IT infrastructures.
Key Features:
- Monitors and exports data to text files
- Attacks fake access points
- Packet Capture Monitoring
- Access Point Manipulation
- Wi-Fi Compatibility Testing
Benefits:
- Cracks WiFi passwords using various techniques including WPS attacks, brute force, and dictionary attacks.
- Operates across multiple platforms such as Windows, macOS, Unix, and Linux.
- Comes pre-installed in Kali Linux, facilitating immediate use.
Limitations:
- Not suitable for beginners due to its complex and advanced requirements.
- Often detected and blocked by network security measures such as firewalls, authentication, or encryption
3. Encryption Tools
Data encryption tools employ advanced algorithms to scramble plaintext data, converting it into meaningless text. This encrypted data is then protected by a unique key or password, making it inaccessible to anyone without the proper decryption credentials. This process ensures that the sensitive information remains confidential and secure.
-
AxCrypt
AxCrypt is a user-friendly solution that provides a set of tools for protecting sensitive data and ensuring security. It secures files with 128-bit or 256-bit AES encryption and offers convenient mobile app access. Additionally, it stores and manages encrypted files in the cloud with the integration of services like Dropbox, AWS and Google Drive.
Key Features:
- Strongest standardized encryption
- Password Management
- Supports multiple languages for global user base.
- Monitors Secured folders
Benefits:
- Allows user verification of code for complete transparency.
- Supports opening encrypted files without the software, offering high flexibility and ease of access on any PC.
- Generates encryption keys easily, simplifying secure access to encrypted files.
Limitations:
- Lacks full macOS feature parity, providing fewer options compared to Windows.
- Suffers from an outdated user interface in its desktop application.
-
VeraCrypt
VeraCrypt is encryption software available for Windows, Linux, and macOS. It encrypts data by utilizing specific details such as location and volume size, allowing users to encrypt an operating system, an entire partition, or create a virtual encrypted disk. This tool is recognized for its robust features that provide comprehensive encryption solutions.
Key Features:
- Encrypted Virtual Disks
- Hidden Data Protection
- Dual Encrypted OS
- Real-Time Encryption
Benefits:
- Secures entire storage devices, including USBs and hard drives.
- Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information, mitigating risks of financial loss and data leaks
- Works alongside antivirus software to keep encrypted data safe even if malware infiltrates the system.
Limitations:
- Takes considerable time for the initial setup of an encrypted file-hosted volume.
- Requires complex handling, making the encryption process challenging for users.
-
7-Zip
7-Zip is a free and open-source tool that compresses a collection of files while preserving their original format. Moreover, it offers ideal read and write capabilities across various archive formats. Its primary function is to reduce file size while maintaining data quality, making it a perfect solution for efficient file management.
Key Features:
- Higher compression ratios especially with the 7z format.
- Strong AES-256 encryption for secure file compression and archiving
- Worldwide accessibility over 80 languages
Benefits:
- Features a user-friendly interface, making it easy to navigate for all skill levels.
- Seamlessly integrates with Windows Shell, allowing direct compression and extraction from the context menu.
- Provides free, open-source access with no licensing fees or restrictions
Limitations:
- Lacks Native Mac and Linux Support, relying on unofficial ports with limited functionality.
- Compresses files slowly when using the 7z format with maximum compression settings.
3. Penetration Testing Tools
A penetration test is a controlled and authorised cyberattack simulation. It helps identify vulnerabilities and assess how attackers could exploit them, ultimately enabling organisations to understand and mitigate business risks. The test evaluates system defences against a wide range of threats. These testers identify weaknesses through authenticated and unauthenticated access roles.
Let us understand these tools in detail.
-
Kali Linux
Kali Linux is a leading cybersecurity platform that provides various tools for companies to safeguard their networking systems. With over 300 tools, security professionals can monitor and identify vulnerabilities, ensuring the integrity of their systems and protecting against potential threats.
Key Features:
- Preinstalled security tools for instant access to essential utilities.
- Broad hardware support, including compatibility with ARM devices.
- Live USB Boot, allowing use without installation on the host system.
Benefits:
- Ensures transparency and flexibility as a free and open-source platform with no licensing restrictions.
- Provides extensive documentation and an active support community for troubleshooting and learning.
- Offers a secure environment for ethical hacking training and cybersecurity skill development
Limitations:
- Difficult for beginners due to its complex interface and advanced tools.
- Legal risks involved if used on networks without proper authorization.
-
Burp Suite
PortSwigger’s Burp Suite is a leading tool for web application penetration testing, widely trusted by security professionals. This comprehensive tool enables experts to assess web application security, discover vulnerabilities and provide recommendations for improvement. Its user-friendly interface makes it a more suitable choice for OWASP ZAP and a preferred choice for those looking for a reliable and efficient security solution.
Key Features:
- Traffic Interception & Modification
- Automated Vulnerability Scanning
- Security Attack Simulation
- Session Authentication Management
Benefits:
- Reveals Hidden Attack Surface by automatically detecting static and dynamic URLs and parameters.
- Scans Passively and Actively to detect vulnerabilities while browsing or targeting specific inputs.
- Generates Automated Reports for quick and simplified security reporting.
Limitations:
- Consumes high resources, leading to slowdowns during complex or large-scale testing.
- Generates false positives, occasionally flagging non-issues in automated scan reports.
-
Metasploit
Metasploit is a powerful toolkit that provides an array of advanced features which is used by both cyber attackers and as well as cyber defenders. It offers a comprehensive database of known vulnerabilities, an extensive library of exploit modules, and a powerful payload framework. Its multi-platform compatibility enhances flexibility, making it suitable for diverse target environments.
Key Features:
- Seamless Integration of Exploit Modules and Payloads.
- Built-in Vulnerability Scanner
- Customizable Payload Framework
- Post-Exploitation Modules
Benefits:
- Offers open-source accessibility with regular updates for enhanced security and functionality.
- Ensures clean exit after penetration tests while enabling persistent access through multiple methods.
- Provides graphical interfaces like Armitage for easy vulnerability management and workspace setup.
Limitations:
- Restricted Shell Access limits command execution and system control.
- Limited to target systems that support its exploits, making it ineffective against patched or updated machines.
- Depends on Public Exploits, making it less effective against unknown or patched vulnerabilities.
Core Capabilities of Cybersecurity Tools
Cybersecurity tools play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data and digital assets. Beyond their individual functions, these tools share fundamental security capabilities that strengthen an organization’s defense against cyber threats. Below are some essential security mechanisms that contribute to their effectiveness.
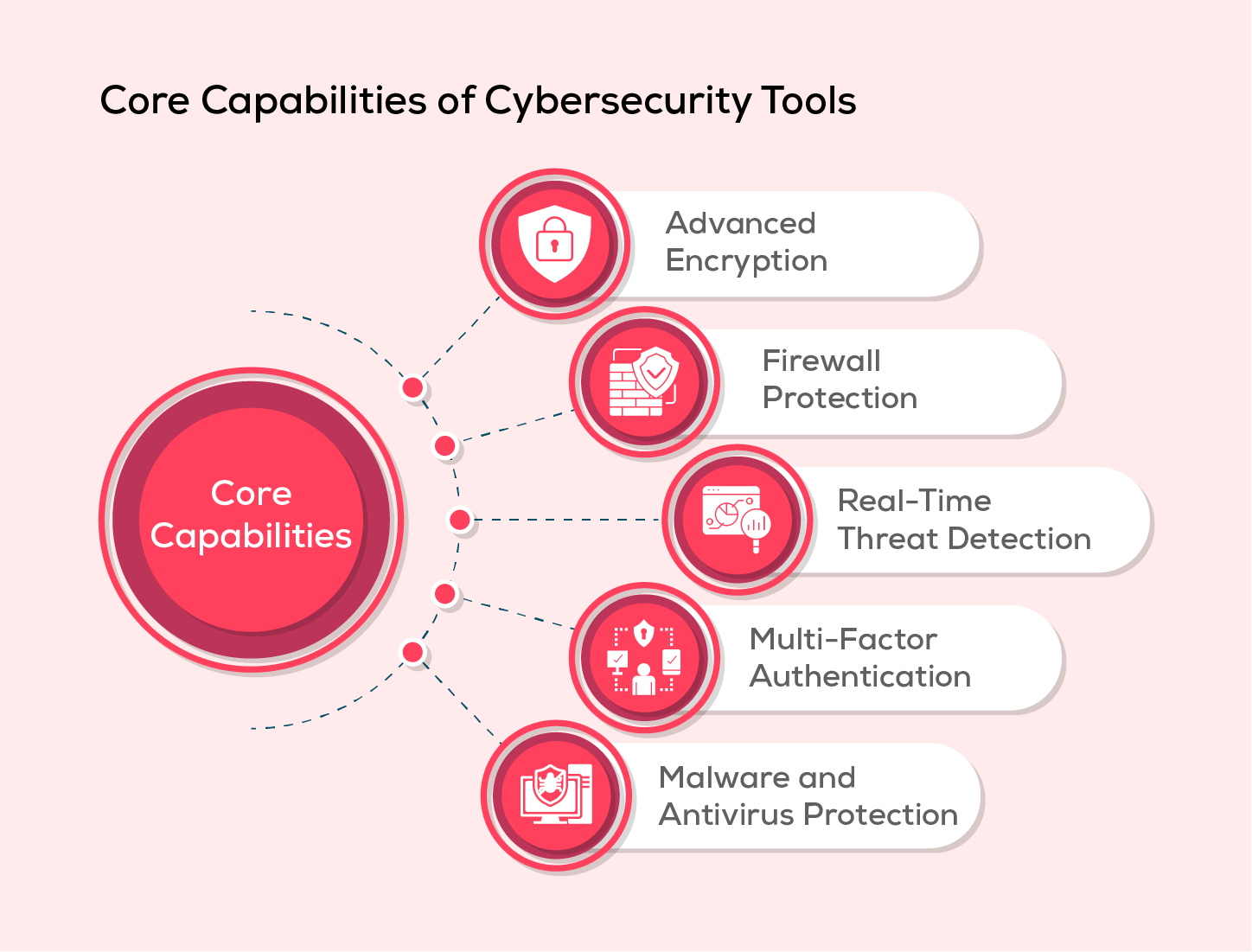
1. Advanced Encryption
Encryption is a critical component of any cybersecurity strategy, providing a powerful layer of protection for sensitive data. Organizations can ensure that it stays inaccessible to unauthorized individuals, even if it is accessed without permission. This security measure provides a strong defence against cyber threats, and protects against data breaches.
2. Firewall Protection
A firewall is a front-line defense of network security, acting as a bridge between an organization's internal networks and the external sources. It controls the flow of data and prevents cyber intrusions. By integrating firewall capabilities, these tools can block malicious traffic and restrict network communications to trusted sources, by ensuring security.
3. Real-Time Threat Detection
Proactive security tools continuously monitor systems for suspicious activity. By identifying and responding to threats in real time, they minimize potential damage and enhance threat mitigation strategies.
4. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication strengthens identity verification by users to provide various forms of proof such as passwords, biometrics resources, SMS-based authentication, facial recognisition, fingerprints or one-time codes, before accessing. This multi-layered approach reduces the risk of unauthorized access, protecting sensitive data and preventing identity theft.
5. Malware and Antivirus Protection
Malware protection is essential for defending against viruses, ransomware, and other malicious software. Effective cybersecurity tools detect, isolate, and remove threats before they can compromise a system.
How to select the right Cybersecurity Tool?
Selecting the best cybersecurity tool is paramount in protecting digital information. With so many options available in the market it is imperative to select a tool that aligns with your specific needs and provides robust protection against cyber threats. Here is the list to help you make the right choice :
- Recognize the security needs: Determine the specific threats and vulnerabilities your organization needs to address.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the tool: Assess how well the tool detects, prevents, and responds to cyber threats.
- Assess user experience: Consider ease of use, interface intuitiveness, and learning curve.
- Ensure Adaptability: Choose a tool that integrates well with existing systems and scales as needed.
Meet Regulatory Requirements: Ensure the tool aligns with industry regulations and data protection standards.
Summing up
The digital era has unlocked countless advantages but has also introduced a new landscape of cyber threats. As the risk of cyberattacks increases, so does the need for cybersecurity tools. By implementing these tools, individuals and organizations can safeguard themselves from breaches and ensure a secured digital landscape.
By deploying the right cybersecurity tool, organizations can shift from a reactive to a proactive approach. This enables them to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals, by reducing the risk of security incidents and preserving digital assets.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long does it take to integrate with the cybersecurity tool and set up a program?
The integration timeline varies depending on the existing infrastructure, the tool’s complexity and readiness. Smaller business requires almost 1-3 months while larger enterprises need 6-12 months to complete the process.
2. Why is it risky to use outdated cybersecurity tools?
Using outdated cybersecurity tools leaves organizations vulnerable to emerging threats. Without updates, they fail to patch security gaps, increasing the risk of data breaches, malware attacks, and unauthorized access.
3. What are the 5Cs of cybersecurity?
The 5Cs of cybersecurity are compliance, cost, coverage, continuity, and change—key focus areas for organizations. They ensure regulatory adherence, budget efficiency, security implementation, business continuity, and adaptability to evolving threats.
4. What’s the difference between encryption and hashing?
Encryption and hashing both convert readable data into an unreadable format, but with key differences. Encryption allows data to be decrypted back to its original form, while hashing is irreversible. Both are essential for protecting data from breaches and identity theft.
5. How can machine learning improve the effectiveness of cybersecurity tools?
Machine learning improves cybersecurity by automating threat detection, recognizing patterns, and detecting anomalies in real time. It allows systems to anticipate and counter cyber threats proactively, minimizing false positives and increasing detection accuracy. Integrating machine learning helps organizations bolster their defenses against emerging threats and accelerate response efforts.