Quick Summary: Your network might appear secure, but unseen vulnerabilities could silently put your organization at risk. Vulnerability scanning ensures nothing goes unnoticed, from minor weaknesses to critical flaws. By automating the detection process, prioritizing risks based on severity offers actionable solutions and ensures your defenses are always one step ahead. This article highlights the significance of vulnerability scanning in identifying and addressing security gaps, providing actionable insights to strengthen defenses and ensure proactive protection against emerging threats.
With cyber threats constantly evolving and compliance requirements intensifying, businesses must proactively manage their security to stay protected against potential risks. This is where vulnerability scanning becomes essential — it serves as your organization's key tool in detecting and addressing security flaws before cybercriminals can take advantage of them.
Vulnerability scanners automatically asses the systems, networks and applications for weaknesses that could jeopardise the organization. The right tools, offer real-time insights into the security posture, enabling quick and proactive responses.
Why wait for a breach to occur? Regular vulnerability scans allow us to identify and mitigate potential risks, safeguarding sensitive information and enhancing security posture.
What is Vulnerability Scanning?
Vulnerability scanning plays a crucial role in the maintenance of IT security. By utilizing specialized software tools or services, this automated process scans computer systems, networks, or applications to uncover known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and other security gaps that cyber attackers could potentially exploit.
The purpose of these scans is not just to identify but also to prioritize these security risks based on their severity. This strategic assessment allows organizations to swiftly address and rectify critical vulnerabilities, thus preventing cybercriminals from exploiting them. Regularly conducting these scans ensures that an organization’s IT infrastructure remains protected against evolving threats, aligning with security best practices and compliance requirements.
Types of Vulnerability Scanners
As organizations navigate escalating cybersecurity challenges, particularly with the surge in remote work— security teams have become increasingly reliant on the right tools for adequate protection. Vulnerability scanners are essential for identifying security weaknesses. They come in various forms, each tailored to address specific types of vulnerabilities.
Let’s explore the common types of vulnerability scanners and see how each plays an important role in protecting the organization.
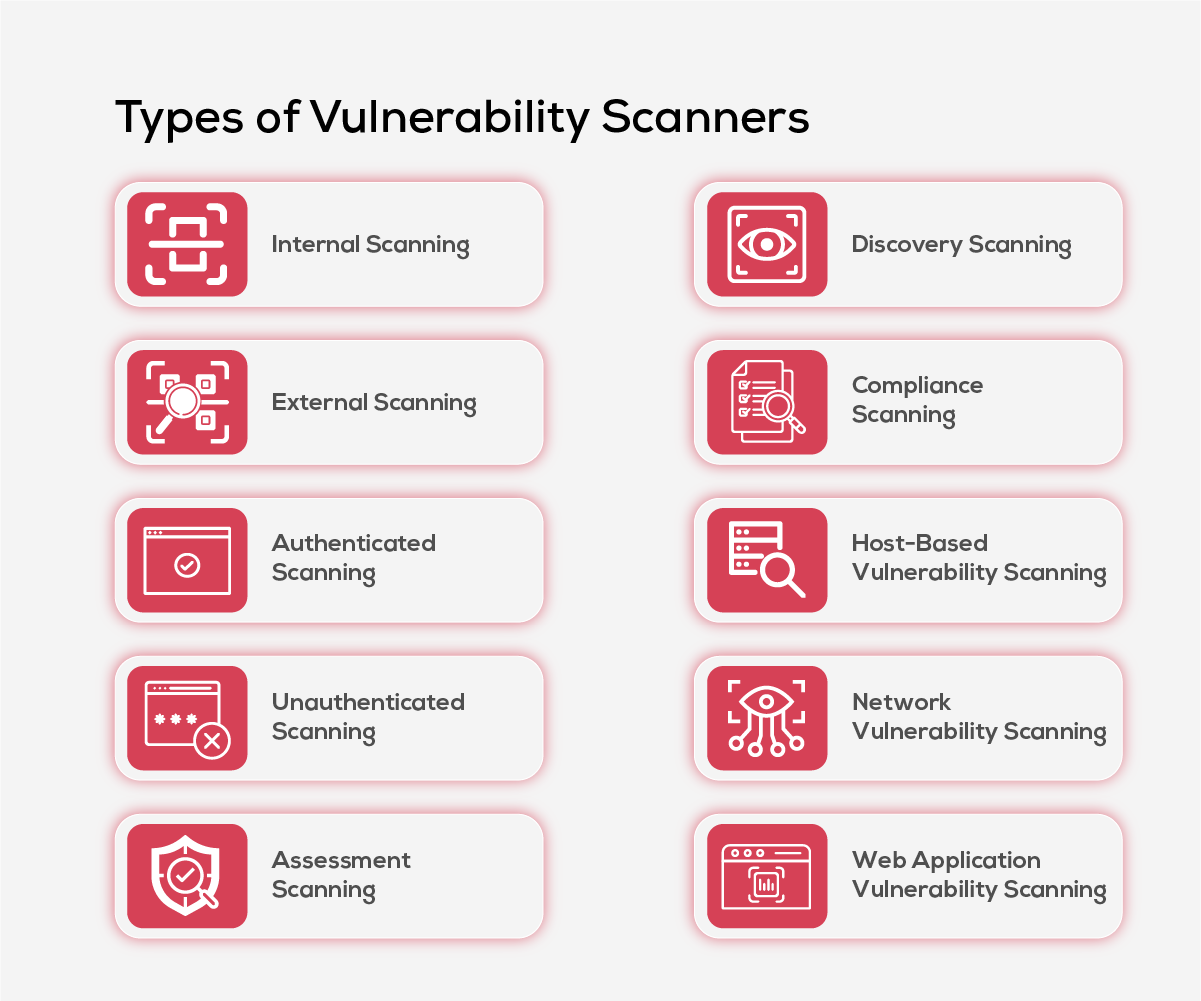
1. Internal Scanning
An internal vulnerability scanner is a specialized security tool designed to analyse the internal systems, servers and applications within an organization’s network. It identifies possible vulnerabilities, such as outdated software, misconfiguration settings and weak passwords that could be targeted by malicious actors, including those within the organization itself, thus addressing potential insider threats.
This type of scanner uses methods such as asset discovery, vulnerability signature matching, exploitation testing and configuration auditing to detect vulnerabilities and evaluate the potential possibilities of attacks.
Advantages:
- Automated scanning
- Improved security posture
- Risk prioritization
2. External Scanning
External vulnerability targets susceptibilities outside the organization’s network, it scans publicly accessible systems to identify weaknesses such as open ports and outdated software. Unlike penetration testing, which actively exploits these vulnerabilities to simulate an attack, external scanning focuses on the detection and categorization of these vulnerabilities. Once risks are identified, the vulnerabilities are categorized and prioritized based on severity, ensuring that significant security gaps are addressed with precision.
Advantages:
- Early threat detection
- Detailed reporting
- Compliance verification
3. Authenticated Scanning
Authenticated scanning leverages valid user credentials to gain deeper access into systems and applications. This approach enables a comprehensive assessment of configuration settings, software versions, and other critical details that are only accessible when logged into the system. By simulating the level of access granted to users, authenticated scanning can accurately detect security gaps that are specific to user permissions and roles, guaranteeing that critical issues tied to access levels are identified and addressed.
Advantages:
- Precise and accurate results
- Insider threat detection
- Deeper visibility
4. Unauthenticated Scanning
As the name suggests, unauthenticated scanning conducts vulnerability assessments without the use of any credentials or user accounts. Typically executed from an external viewpoint, this type of scan assesses the security of internet-facing systems, including web applications, public network infrastructure and websites. It aims to identify weaknesses that are detectable without privileged access, including open ports, server misconfiguration and outdated software versions.
Advantages:
- Less resource intensive
- Early detection
- Ideal for public-facing systems
5. Assessment Scanning
This type of scanning offers a thorough evaluation of an organization’s network and systems security. It incorporates methods such as configuration analysis, vulnerability detection and compliance verification. The primary goal is to analyse the organization’s IT infrastructure, detect security deficiencies and discover potential areas for security enhancements.
Advantages:
- Automated Process
- Regular Monitoring
- Cost Reduction
6. Discovery Scanning
Discovery scanning aims to identify servers and assets connected to the network. It offers organizations a clear understanding of their network structure, highlighting any unauthorized or any unmanaged devices. This scan serves as the first step in vulnerability assessments and security measures, ensuring a comprehensive approach to network security management.
Advantages:
- Early Vulnerability Detection
- Identifying Unauthorized Devices
- Minimal Network Impact
7. Compliance Scanning
Assessing systems and networks to confirm their alignment with established security standards is a key aspect of compliance scanning. This type of scanning thoroughly checks that an organization’s IT infrastructure adheres to industry best practices and regulatory requirements, minimizing the potential risks associated with non-compliance.
Advantages:
- Continuous monitoring
- Data protection
- Risk prioritization
8. Host-Based Vulnerability Scanning
Host-based scanning targets individual devices, such as servers, endpoints, or workstations to identify vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. It evaluates the unique attributes of each host, including installed software, system settings and active services. This approach is necessary for detecting vulnerabilities specific to each device or operating system, facilitating targeted and effective security measures.
Advantages:
- Internal Attack Detection
- Improved Patch Management
- Targeted Remediation
9. Network Vulnerability Scanning
Network scanning detects active devices, open ports, and potential security vulnerabilities. This process enables organizations to understand their network’s structure and identify potential access points for cybercriminals. It serves as a critical component in managing network security and assessing risks.
Advantages:
- Improved network visibility
- Proactive security
- Vulnerability detection
10. Web Application Vulnerability Scanning
Web application scanning assesses the security of web applications and services on web servers. It identifies risks including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and flawed authentication procedures. Essential for enhancing web application security, this scanning helps shield against prevalent hacking strategies targeting web servers.
Advantages:
- Integration with CI/CD pipeline
- Data security
- Scalability
How does Vulnerability Scan Work?
Automated tools are used during the scanning process to identify potential vulnerabilities that could be targeted by attackers. This approach allows a web application vulnerability scanner to thoroughly inspect every section of the website, ensuring that all potential weaknesses are identified.
Here’s a quick look at how vulnerability scanning typically unfolds:
1. Asset Discovery
Initiating a thorough vulnerability scan requires an up-to-date asset inventory. As the critical first step, asset discovery unveils the complete attack surface of a network. This phase involves systematically identifying and cataloging every asset within the network, ensuring that no critical components are overlooked. By accurately capturing all network elements, organizations can proactively address vulnerabilities, thwarting potential exploits by attackers before they occur.
2. Enumeration
Once the assets are identified, the vulnerability scanner performs enumeration to gather details about these assets, such as open ports and the services running on them. This process gives a clear picture of the attack surface, setting the stage for a more targeted vulnerability assessment.
3. Vulnerability Detection
The scanner then analyzes the gathered information against an up-to-date database of known security flaws. Updating this database regularly ensures effective detection of both existing and emerging vulnerabilities, helping organizations stay ahead of potential threats.
4. Assessment
Once vulnerabilities are detected, they are categorized by severity. Tools like the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) help assign numerical scores to these vulnerabilities, prioritizing them so that the most critical issues can be addressed first. This prioritization is essential for efficient resource allocation and risk management.
5. Reporting
The process culminates with detailed reports that outline discovered vulnerabilities, including their severity, potential impact, and recommended remedial actions. These reports are instrumental for security teams to assess and plan their mitigation strategies, ensuring a systematic response to security risks.
6. Remediation
After identifying vulnerabilities, organizations take proactive steps to mitigate the risks by applying patches, reconfiguring systems, updating software, or implementing additional security measures. This stage is vital for closing security gaps and enhancing the overall security framework.
7. Continuous Monitoring
Security is an ongoing process, and new vulnerabilities can arise over time existing protections may become outdated over time. Regular vulnerability scans are essential to maintain an up-to-date understanding of a system or networks security posture, keeping security measures aligned with emerging threats.
Benefits of Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanning provides indispensable benefits for businesses across the spectrum by actively scanning and mitigating security risks. This strategic tool plays a vital role in strengthening security frameworks and ensuring regulatory compliance.
1. Quick Flaw Detection
Vulnerability scanners enable organizations to detect security weaknesses and flaws in the systems, networks and applications before they can be exploited by hackers and other malicious entities. This approach enables timely intervention, reducing the likelihood of cyberattacks and data breaches.
2. Stronger Security
The regular application of vulnerability scanners helps organizations strengthen their security posture by continuously scanning for new weaknesses and changes in their environment. This forward-looking strategy empowers organizations to stay ahead of potential threats and uphold robust security vigilance.
3. Strategic Risk Management
These tools meticulously assess and report vulnerabilities, enabling businesses to strategically prioritize their security initiatives. This focused management of resources tackles the most pressing threats first, drastically cutting down the organization's exposure to cyber risks.
4. Improved Efficiency
Rapid scanning processes cover extensive and intricate networks efficiently, liberating IT teams to focus on more strategic projects. This efficiency minimizes the need for constant manual oversight, allowing personnel to intervene only for critical updates or issues, thus maximizing productivity.
5. Lower Costs
Automated vulnerability scanning provides a cost-effective approach to security, by reducing the need for frequent manual checks. Systematic and regular scans help avert expensive data breaches and lower the costs associated with managing security incidents, making it a financially savvy choice for maintaining long-term security.
Summing Up
As organizations increasingly depend on big data and digital technologies, identifying and mitigating security vulnerabilities becomes paramount. Vulnerability scanners offer a robust solution, enabling businesses of all sizes to safeguard their networks and confidential data effectively. Considering the diverse range of scanners available, from those targeting databases to host systems, it's essential to thoroughly evaluate one’s unique requirements to choose the most suitable tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s the difference between a vulnerability scan and a security scan?
A vulnerability scan is specifically aimed at detecting security weaknesses in software and systems. In contrast, a security scan is a more comprehensive term that encompasses vulnerability scanning as well as various other methods, including port scanning, network mapping, and web application scanning.
2. What are the top Vulnerability Scanning tools in cybersecurity?
Vulnerability scanning tools enhance an organization's security stance by offering automated scanning features, comprehensive reporting and the ability to integrate with other security solutions. Some of the tools include OpenVAS, Burp Suite, Nessus and Nexpose.
3. How often should I perform a Network Vulnerability Scan?
Every business has unique requirements, but it is generally recommended to conduct vulnerability scans at least quarterly. Depending on factors such as compliance regulations, significant infrastructure changes, and the organization's internal network security measures, more frequent scans—such as monthly or even weekly—may be necessary.
4. How do integrations enhance vulnerability assessment scanning?
Integrating vulnerability scanning tools with existing security systems ensures smooth operation within your cybersecurity framework. This simplifies security management, enhances protection, and creates a more unified defense strategy.
5. Can vulnerability scanners produce varying results?
Yes, the detected vulnerabilities can differ depending on the scanning method used. Certain vulnerability scanners allow for customized scans, leading to variations in the results.